In today’s mobile-first world, protecting user data while allowing seamless app-to-app communication is essential. Android addresses this need through Content Providers, a powerful framework that enables applications to share structured data in a secure and standardized way.
At the center of this system is the Content URI a special identifier that points to data managed by a Content Provider. In this guide, we’ll explain what Content URIs are, how they function, and why they’re important, using the following real example:
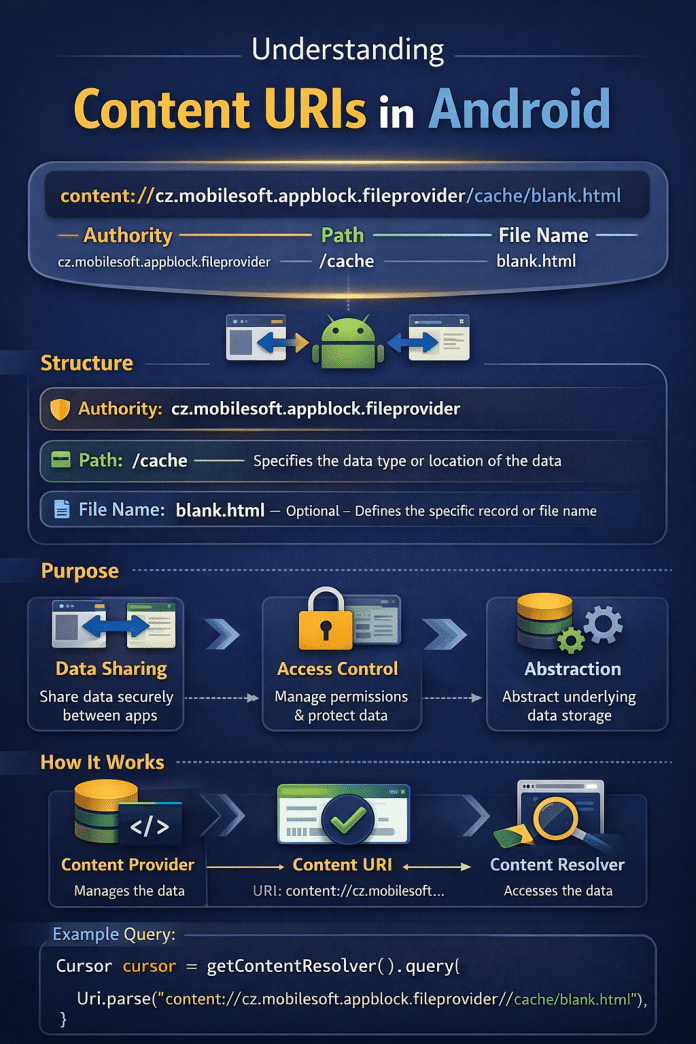
content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html
By the end, you’ll understand its structure, purpose, and how developers rely on Content URIs to safely manage and exchange data.
What Is a Content URI?
A Content URI is a unique address used within Android to locate and access data provided by a Content Provider. Unlike traditional file paths, which depend on device-specific storage layouts, Content URIs offer a stable and secure way to reference data across applications.
They are commonly used for:
- Sharing files between apps
- Accessing system data (contacts, media, calendars)
- Hiding internal storage structure
- Enforcing permission-based access
Structure of a Content URI
A typical Content URI follows this pattern:
content://<authority>/<path>/<id>
Components Explained
| Component | Meaning |
| authority | Identifies the Content Provider (usually the app’s package name) |
| path | Indicates the data category or directory |
| id | Optional identifier for a specific item |
Example Breakdown
content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html
- Authority: cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider
- Path: cache
- File Name: blank.html
This tells Android to fetch a file named blank.html from the cache folder managed by the AppBlock file provider.
Why Content URIs Are Important
Content URIs play a critical role in Android app architecture:
🔁 Safe Data Sharing
Applications can exchange data without exposing internal storage paths.
🧩 Flexible Architecture
Developers can change how data is stored internally without breaking external access.
🔒 Built-In Security
Permissions and access rules prevent unauthorized usage.
Understanding Content Providers
A Content Provider is an Android component that controls access to a shared dataset. It acts as a mediator between apps and data sources.
Key Features
- Supports Create, Read, Update, and Delete (CRUD) operations
- Offers a consistent interface for data access
- Enables inter-application communication
Common Examples
- Contacts and calendars
- Images, videos, and audio files
- App-specific shared storage
What Is a File Provider?
A File Provider is a specialized type of Content Provider designed specifically for sharing files. Instead of revealing real file paths, it generates secure Content URIs that grant limited, temporary access.
This approach protects internal storage from unrestricted exposure.
How Developers Work with Content URIs
1. Create a Content Provider
public class MyContentProvider extends ContentProvider {
// Implement query, insert, update, delete methods
}
2. Register It in AndroidManifest.xml
<provider
android:name=”.MyContentProvider”
android:authorities=”cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider”
android:exported=”true” />
3. Access Data Using ContentResolver
Cursor cursor = getContentResolver().query(
Uri.parse(“content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html”),
null, null, null, null
);
if (cursor != null) {
while (cursor.moveToNext()) {
// Handle retrieved data
}
cursor.close();
}
Securing Access with Permissions
Developers can restrict access by assigning custom permissions:
<provider
android:name=”.MyContentProvider”
android:authorities=”cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider”
android:permission=”cz.mobilesoft.appblock.permission.ACCESS_DATA”
android:exported=”true” />
Only applications granted this permission can access the provider.
Best Practices for Using Content URIs
✔ Design clear and consistent URI structures
✔ Use meaningful and descriptive paths
✔ Clean up cache files regularly
✔ Protect sensitive data with permissions
✔ Test access from multiple scenarios
Conclusion
Content URIs form the backbone of Android’s secure data-sharing model. They provide a standardized, flexible, and safe way to expose information across applications.
The example:
content://cz.mobilesoft.appblock.fileprovider/cache/blank.html
shows how Android combines abstraction, security, and accessibility into a single reference.
By mastering Content Providers and Content URIs, developers can build robust, future-ready Android apps that handle data responsibly and efficiently.